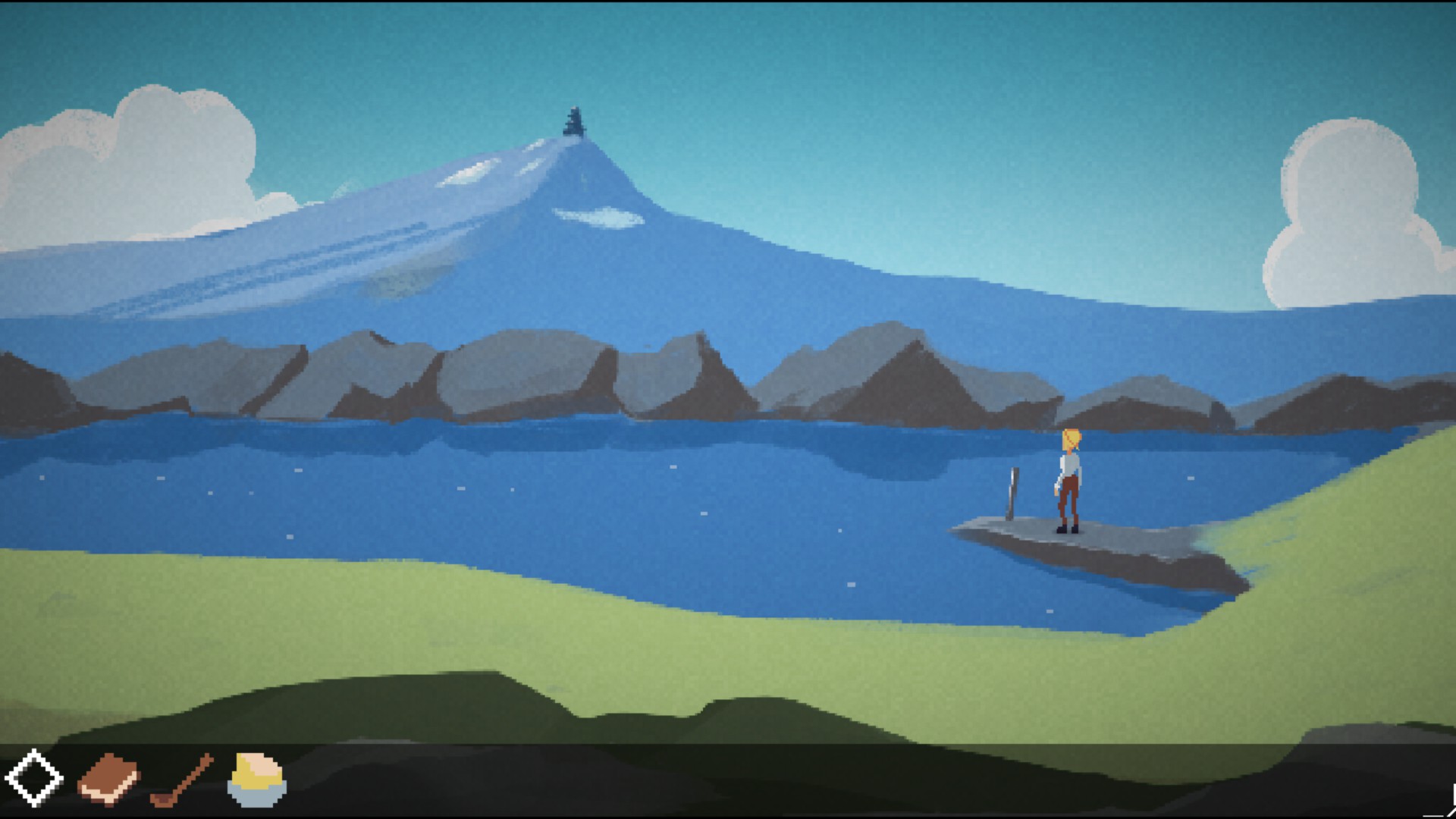
Milkmaid of the Milky is a 90s style point-and-click adventure, where you play as a milkmaid on a journey to save her cows. Developed by Mattis Folkestad of Machineboy (essentially a one man team), Milkmaid of the Milky Way is a labour of love. And I think it shows. It has evocative visuals, amazing music, and is written entirely in rhyming verse. Passion was poured into this game, and it’s better for it.
Milkmaid of the Milky Way is both whimsical and melancholy. A story about being alone and coming together. The protagonist, Ruth, lives alone on a small farm. Her only companions are cows, but she is devoted to them. When a spaceship shows up and abducts her bovine friends, she vows to go save them. Here is where the story takes off, and I don’t want to say anymore for fear of spoiling it, but things get much more complicated as the story twists and turns.
The dialogue is written in rhyme, and coupled with the hand drawn backgrounds, the game has a storybook feel.
Despite the spaceships and cows, the story is about moving on, fighting loneliness, and asking when your responsibilities are infringing on your life and happiness. It’ll leave you wondering if you’ll have any regrets when you’re older, and maybe put a fear of stagnation in you.
On PC the game controls like most point-and-clicks. You move by clicking on an area of the world, and you can double click to run. This is a nice feature that keeps you from lumbering back and forth as you traverse the environments, especially when you have to do some backtracking. You also click to examine or interact with an object (including items in your inventory), and dragging items from your inventory onto an environmental object will let you use it on the object.
The cursor also helps identify interactable elements by pulsating when you hover over them.
The puzzles are straightforward and not too difficult to figure out. Whenever I was stuck, I found myself backtracking a little more than I would have liked, but the run feature went far in alleviating that minor stressor.
The components of the puzzles fit nicely into the world. When Ruth uses a wooden spoon to reach something, or her knowledge gained from farm work to solve a problem, it’s believable. The puzzles never felt abstruse or out of place.
Milkmaid of the Milky Way is a beautiful game. Its characters are all endearing, and it manages to communicate personality through visual cues and terse dialogue. It’s a tightly made package, with a strong story, evocative music, and gorgeous visuals.
I highly enjoyed it and would recommend anyone looking for a point-and-click adventure to check it out.
Buy Milkmaid of the Milky Way on Steam for PC and Mac, or on iTunes for iOS.
You can find Mattis Folkestad on twitter, at Machineboy.com, or visit Milkmaid of the Milky Way’s official site.
I was provided with a free copy for review.